Modeling
Contents
AUTOSAR META-MODEL
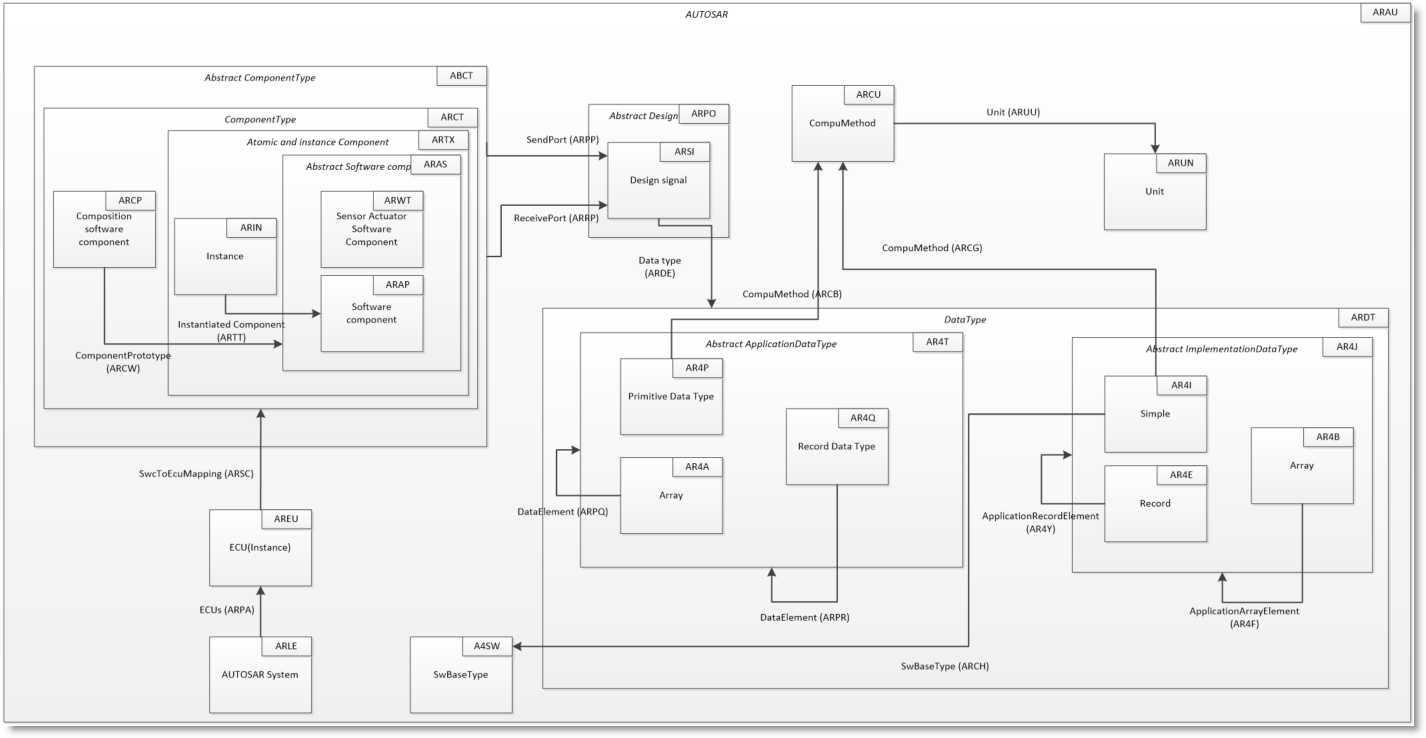
Above is the basic SystemWeaver Autosar Meta Model
Components
The component types used include:
Software component: Represents the software logic
Sensor Actuator Software Component: Represents the interface to the hardware (abstraction of the driver)
Connection Model
The connection model used is implicit. This means that if one component sends a specific interface and another component receives the same interface the components are connected through that interface.
Data Types
There are two types of data types. In some cases both are needed, for instance, when developing software that can run on different types of hardware (i.e., with floating point and without floating point processor)
Implementation Data Type
This type is used when implementing an ECU. It has both a CompuMethod describing the data type and a swBaseType describing the representation of the data type, e.g., uint8, int32, etc.
Application Data Type
This type is used to give input to do a signal database and when implementation is done later. It does not have a swBaseType since the specific representation of the signal is decided when designing the network.
ROS META-MODEL
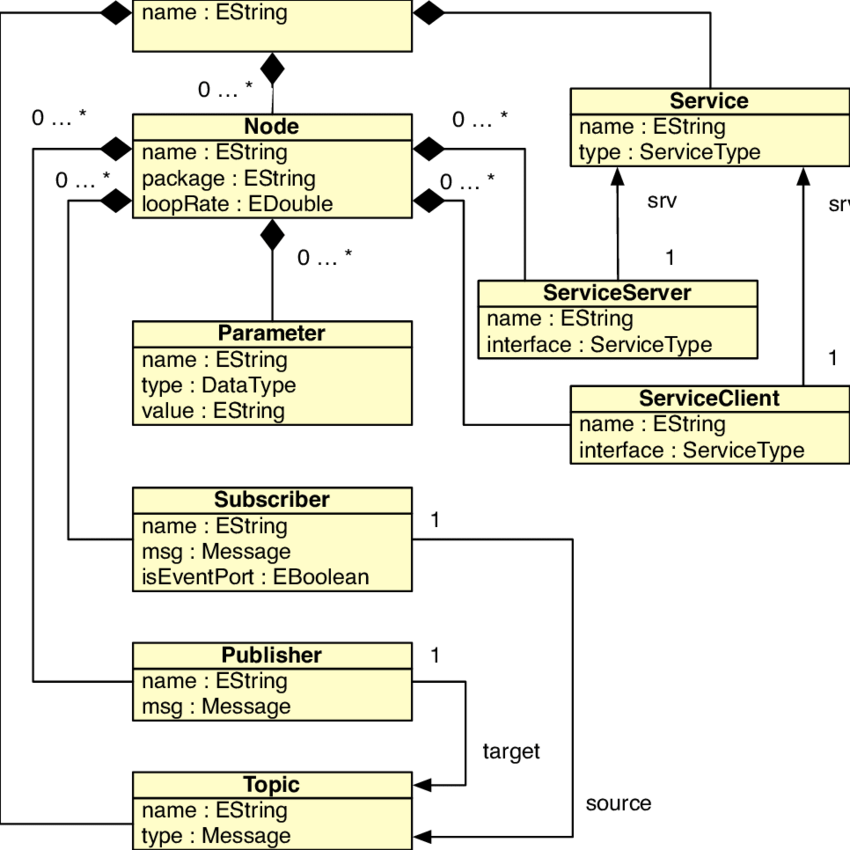
The ROS component meta-model
Nodes in ROS
Each node in ROS should be responsible for a single, module purpose (e.g. one node for controlling wheel motors, one node for controlling a laser range-finder, etc). Each node can send and receive data to other nodes via topics, services, actions, or parameters.
A Node is the ROS equivalent of a component and is a stand-alone executable. The reference to its implementation is defined by means of twovalues: thepackageand thename. In ROS a package is a folder containingthe implementation of software libraries and nodes, which are characterizedby their name. The couple package-name has to be unique in the ROS filesystem and identify the implementation of a node. Changing these values allows us to change the node implementation. Nodes provide four kinds of interfaces: Publishers, Subscribers, Service Servers and Service Client.
Publisher and Subscriber are interfaces (respectively provided and re-quired) that can be used for implementing a communication based on thePublish-Subscriber style. The connection between a publisher and a sub-scriber is realized by means ofTopics, which are named buses over whichnodes exchange data. They are typed by messages (ROS data structure). A Node publishes on a Topic through a Publisher while subscribes to a Topicthrough a Subscriber. Topics allow several publishers and several subscribers.
Service Server and Service Client are interfaces (respectively provided andrequired) that can be used for implementing a communication based on theClient-Server style. The connection between a Service Server and a ServiceClient is realized by means of aService, which defines the contract between the two entities in terms of two messages: the request and the response.
Finally Nodes can be configured through theirParameters, which are the ROS equivalent of the Properties.
It has to be noted that the Connection defined in the Abstract meta-model can be modeled in ROS by means of the triplet: Publisher.target, Topic, Subscriber.source or the triplet: ServiceClient.service, Service, Service-Server.service.
Variability Modeling and Resolution in Component-based Robotics Systems